Construction of topological maps from a series of multi-focal images
Spring 2004
Master Semester Project
Project: 00076
Extended depth of focus algorithms are common methods to obtain in focus microscopic images of 3D objects and organisms.
They merge a stack of photographs taken at different focal lengths into a single totally focused composite 2D image. Our laboratory recently has developed a wavelet-based approach.
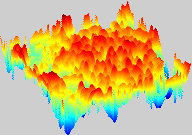
This project extends the current approach. The goal is to recover the 3D topology of the original object. First, for each image in the stack the in-focus areas have to be detected. This can be done with wavelet bases or a redundant wavelet frame approach. From the in-focus areas and the z-position in the respective stack, a topological map can be composed. Adequate consistency checks and interpolation in z-direction allow to construct the 3D topology of the specimen.
Since this reconstructed 3D object is convex by construction, the totally focused composite image can be projected onto the surface. This gives a well interpretable visualization of the specimen.
The method shall be implemented in Java as an ImageJ plugin. It shall be evaluated with respect to an artificial model as well as on real biological data.
Further reading: Extended depth of focus
This project extends the current approach. The goal is to recover the 3D topology of the original object. First, for each image in the stack the in-focus areas have to be detected. This can be done with wavelet bases or a redundant wavelet frame approach. From the in-focus areas and the z-position in the respective stack, a topological map can be composed. Adequate consistency checks and interpolation in z-direction allow to construct the 3D topology of the specimen.
Since this reconstructed 3D object is convex by construction, the totally focused composite image can be projected onto the surface. This gives a well interpretable visualization of the specimen.
The method shall be implemented in Java as an ImageJ plugin. It shall be evaluated with respect to an artificial model as well as on real biological data.
Further reading: Extended depth of focus
- Supervisors
- Brigitte Forster
- Michael Unser, michael.unser@epfl.ch, 021 693 51 75, BM 4.136