Inverse Problems with ℓ1 Regularization: Extreme Points of the Regularization Polytope and Analysis vs Synthesis Formulations
Automn 2025
Master Semester Project
Project: 00463
Context
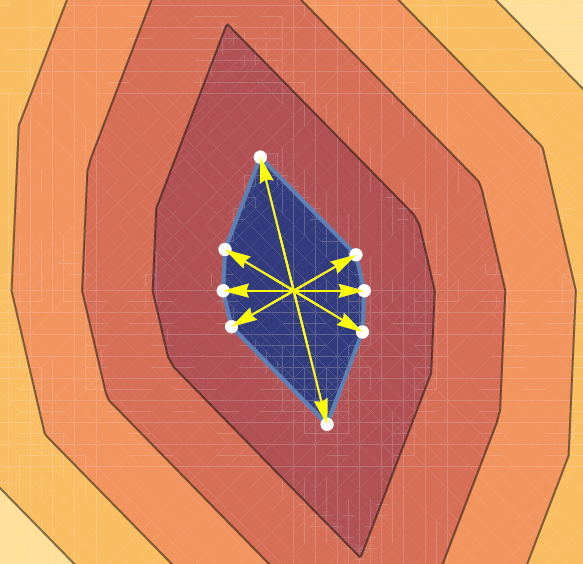
Inverse problems aim to recover a signal from noisy linear measurements by solving an optimization problem with a data-fidelity and regularization term. Regularization enforces a certain prior (a desired "shape") on the solution. For example, ℓ1 regularization promotes sparse solutions, and in finite dimensions, the solution set of such inverse problems is known to be the convex hull of the extreme points of the ℓ1 ball. More generally, a regularization operator L (an m x D matrix) can be incorporated to further dictates the shape of the solution x, ensuring that the vector Lx is sparse. The solution set becomes the convex hull of the extreme points of the regularization polytope {x ∈ Rᴰ : ||Lx||₁ ≤ 1}. Solutions are thus sparse in the dictionary defined by these extreme points.
Projet Outcome
The goal of the project is to determine the extreme points of this regularization polytope defined by a regularization operator L. This helps analyze solution structure and enables a synthesis formulation of the inverse problem. The student is first expected to study the background on inverse problems, ℓ1 regularization and sparsity, and the effects of L. Then, given a regularization operator L (of any size, possibly big), the student will have to design and implement an algorithm to compute the extreme points of its regularization polytope. Depending on the student's advancement and interest, other types of inverse problems can be considered.
Requirements
Programming skills and a good grasp of linear algebra and analysis. Familiarity with image/signal processing is a plus, familiarity with optimization is a plus, familiarity with ML is a plus.
Inverse problems aim to recover a signal from noisy linear measurements by solving an optimization problem with a data-fidelity and regularization term. Regularization enforces a certain prior (a desired "shape") on the solution. For example, ℓ1 regularization promotes sparse solutions, and in finite dimensions, the solution set of such inverse problems is known to be the convex hull of the extreme points of the ℓ1 ball. More generally, a regularization operator L (an m x D matrix) can be incorporated to further dictates the shape of the solution x, ensuring that the vector Lx is sparse. The solution set becomes the convex hull of the extreme points of the regularization polytope {x ∈ Rᴰ : ||Lx||₁ ≤ 1}. Solutions are thus sparse in the dictionary defined by these extreme points.
Projet Outcome
The goal of the project is to determine the extreme points of this regularization polytope defined by a regularization operator L. This helps analyze solution structure and enables a synthesis formulation of the inverse problem. The student is first expected to study the background on inverse problems, ℓ1 regularization and sparsity, and the effects of L. Then, given a regularization operator L (of any size, possibly big), the student will have to design and implement an algorithm to compute the extreme points of its regularization polytope. Depending on the student's advancement and interest, other types of inverse problems can be considered.
Requirements
Programming skills and a good grasp of linear algebra and analysis. Familiarity with image/signal processing is a plus, familiarity with optimization is a plus, familiarity with ML is a plus.
- Supervisors
- Bassam El Rawas, bassam.elrawas@epfl.ch
- Martin Zach, martin.zach@epfl.ch